What is the difference between the mass and weight of a bowling ball! Mass and weight are often confused but are distinct concepts. Mass refers to the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force exerted by gravity on that mass.
Understanding the difference between mass and weight is essential in various fields, from science to sports. For instance, when discussing a bowling ball, we must differentiate its mass from its weight to comprehend its behavior better. Mass remains constant regardless of location, but weight can change with gravity.
This distinction is crucial for accurate measurements and applications. In this post, we’ll explore these concepts, providing clear explanations and examples to help you grasp the difference. Whether you’re a student, a teacher, or just curious, this guide will clarify these fundamental ideas.

Credit: www.facebook.com
Mass Vs. Weight
Understanding the difference between the mass and weight of a bowling ball is essential. These terms are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. Knowing this difference helps in many fields, from science to everyday life. Let’s explore what sets mass and weight apart.
Key Concepts
The terms mass and weight are often confused, but they are different. Here are some key points to understand:
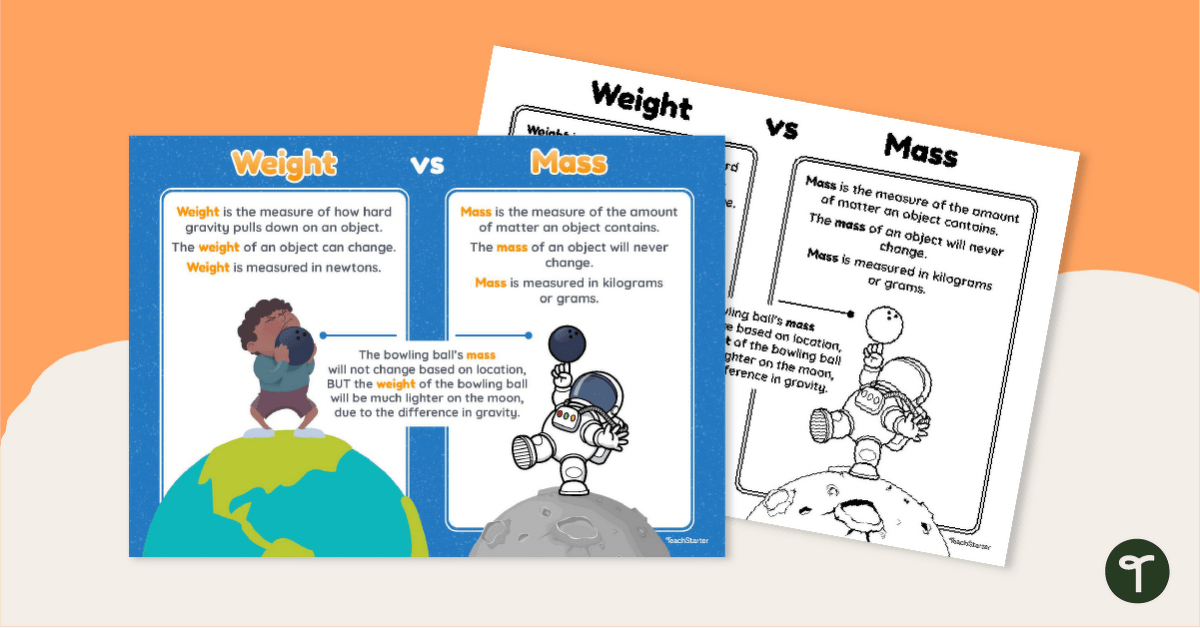
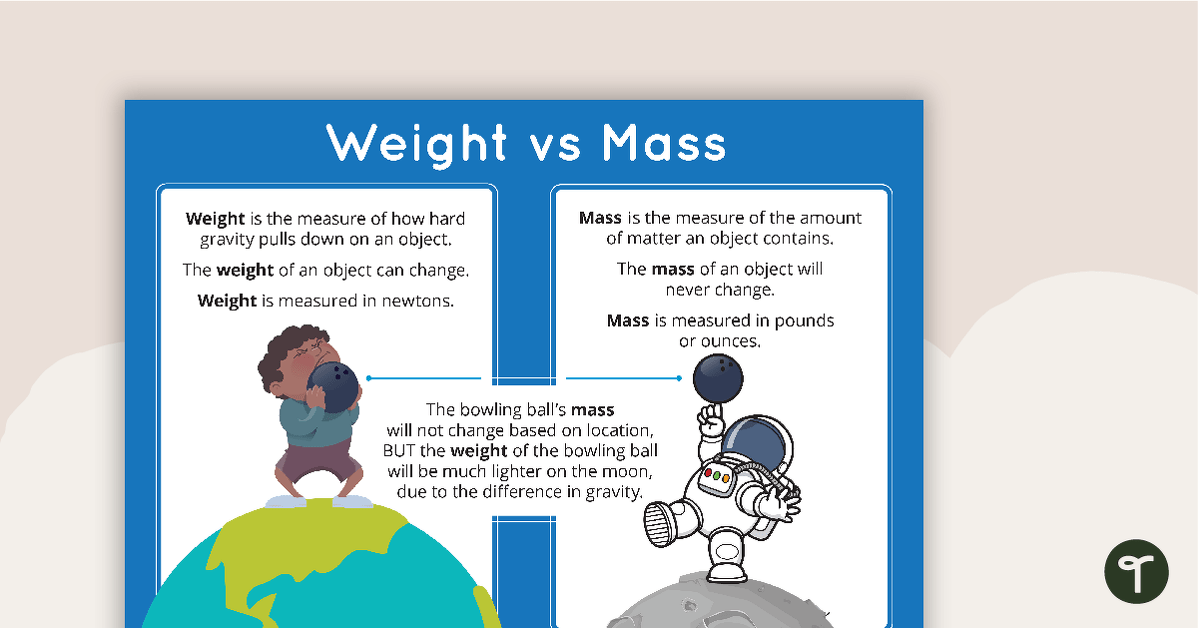
- Mass is the amount of matter in an object. It does not change.
- Weight is the force exerted by gravity on that mass. It can change based on location.
- Mass is measured in kilograms (kg), grams (g), or pounds (lbs).
- Weight is measured in Newtons (N) or pounds-force (lbf).
For example, a bowling ball has the same mass on Earth and the Moon. But its weight differs because gravity is weaker on the Moon. This means the ball will feel lighter on the Moon.
Understanding these concepts helps in fields like physics and engineering. It also helps in daily activities, like knowing how much force is needed to lift an object.
Scientific Definitions
Let’s define mass and weight scientifically. This will help clarify their differences:
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. It is a scalar quantity, which means it has only magnitude and no direction. The unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) is the kilogram (kg).
Weight is a measure of the force exerted by gravity on an object. It is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. The unit of weight in the SI system is the Newton (N).
| Property | Mass | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Amount of matter | Force of gravity |
| Unit | Kilogram (kg) | Newton (N) |
| Type | Scalar | Vector |
| Changes with location? | No | Yes |
These definitions help us understand why mass and weight are different. A bowling ball’s mass remains constant, but its weight varies with gravity.
Credit: www.teachstarter.com
Measuring Mass
Understanding the difference between the mass and weight of a bowling ball can be confusing. Mass is the amount of matter in the ball. Weight is the force of gravity acting on that mass. While mass remains constant, weight can change based on location. This article will help you understand how to measure mass and the units used.
Tools For Measurement
To measure the mass of a bowling ball, you need specific tools. These tools help ensure accuracy. Some of the common tools include:
- Balance Scales: These are traditional tools used to measure mass. The object is placed on one side, and known masses are added to the other side until balanced.
- Electronic Scales: These provide digital readings of mass. They are more convenient and widely used today.
- Spring Scales: These measure weight but can be used to find mass by dividing the weight by the acceleration due to gravity.
Balance scales are often used in laboratories. They are very accurate but require careful handling. Electronic scales are more user-friendly. They are common in homes and businesses. Spring scales are less accurate for mass but useful in physics experiments.
Units Of Mass
Mass is measured in units called grams and kilograms. The gram is the basic unit in the metric system. For heavier objects like a bowling ball, kilograms are used. One kilogram equals 1,000 grams. Other units include:
- Milligrams (mg): Very small units. One milligram is one-thousandth of a gram.
- Metric Ton (t): Used for very large masses. One metric ton equals 1,000 kilograms.
In some countries, pounds and ounces are used. One pound equals 0.453592 kilograms. One ounce equals 28.3495 grams. These units are part of the imperial system.
Knowing these units helps in understanding and converting measurements. This is important for comparing objects in different systems. Understanding mass and weight is fundamental in science and daily life.
Measuring Weight
Understanding the difference between mass and weight can be confusing. This is especially true when discussing objects like a bowling ball. Mass and weight are often used interchangeably, but they mean different things. Mass is the amount of matter in an object. Weight is the force exerted by gravity on that object. Measuring weight involves specific tools and units to get accurate readings.
Tools For Measurement
Various tools are used to measure weight accurately. These tools help determine the weight of objects like a bowling ball.
Some common tools include:
- Scales: The most common tool for measuring weight. There are different types of scales, such as digital and analog scales.
- Spring Scales: These measure weight by the tension of a spring. They are often used in scientific experiments.
- Balance Scales: These compare the weight of an object to known weights. They are very accurate.
Each tool has its own advantages and uses. For example, digital scales are easy to read and use. Spring scales are helpful in educational settings. Balance scales are often used in laboratories for precise measurements. Choosing the right tool depends on the accuracy needed and the context of measurement.
Units Of Weight
Weight is measured using different units. These units depend on the system of measurement being used.
The metric system uses:
- Grams (g): Suitable for lighter objects.
- Kilograms (kg): Commonly used for heavier objects like a bowling ball.
The imperial system uses:
- Ounces (oz): Often used for small objects.
- Pounds (lbs): Commonly used for heavier objects like a bowling ball.
Understanding these units helps in accurate measurement and clear communication. For example, a bowling ball usually weighs around 6 to 16 pounds or 2.7 to 7.3 kilograms. Knowing these units can make it easier to understand and compare weights.
Factors Affecting Mass
Understanding the difference between mass and weight is crucial. Mass measures the amount of matter in an object. Weight is the force exerted by gravity on that mass. These concepts are important when discussing bowling balls. The mass of a bowling ball depends on several factors. These include material composition and size variations. Let’s explore these factors in detail.
Material Composition
The material composition of a bowling ball significantly affects its mass. Bowling balls are made from different materials. These materials include plastic, urethane, reactive resin, and particle. Each material has unique properties and densities.
Plastic balls are the most basic. They are typically used by beginners. Plastic balls have a lower mass because of their density. Urethane balls have higher density than plastic. They offer better control and hook potential. Reactive resin balls are popular among experienced players. These balls have higher mass due to their dense composition.
| Material | Density (g/cm³) |
|---|---|
| Plastic | 0.9 – 1.2 |
| Urethane | 1.2 – 1.3 |
| Reactive Resin | 1.3 – 1.4 |
| Particle | 1.4 – 1.5 |
Choosing the right material affects the ball’s performance. Dense materials increase the mass of the ball. This affects its behavior on the lane. Understanding the material helps in making informed decisions. It helps in selecting the right ball for your game.
Size Variations
Size variations also impact the mass of a bowling ball. Bowling balls come in different sizes, measured by their weight. Common sizes range from 6 to 16 pounds. The size directly correlates with the mass of the ball. Larger balls have more mass. Smaller balls have less mass.
For instance, a 6-pound ball is suitable for children. It has less mass and is easier to handle. An adult might prefer a 14-pound ball. This ball has more mass, providing better control and power. The size selection depends on the player’s strength and skill level.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
- 6-8 pounds: Ideal for children and beginners.
- 10-12 pounds: Suitable for teenagers and women.
- 14-16 pounds: Preferred by adult men and experienced players.
Choosing the correct size is essential. It ensures comfort and effectiveness during play. Heavier balls generate more force when they hit the pins. But they require more strength to control. Lighter balls are easier to handle but may lack power. Understanding size variations helps in selecting the right ball for each player.
Factors Affecting Weight
Understanding the difference between mass and weight of a bowling ball can be confusing. Mass is the amount of matter in the ball. Weight is the force exerted by gravity on that mass. Both are affected by various factors. Let’s look into these factors and see how they influence the weight of a bowling ball.
Gravity’s Role
Gravity plays a crucial role in determining the weight of a bowling ball. Weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object’s mass. The formula to calculate weight is:
Weight (W) = Mass (m) × Gravitational acceleration (g)
On Earth, gravitational acceleration (g) is approximately 9.8 m/s². This means a bowling ball’s weight is directly proportional to its mass. Some important points to consider:
- More mass equals more weight.
- Weight changes with gravity, mass does not.
For example, a 7 kg bowling ball will weigh:
W = 7 kg × 9.8 m/s² = 68.6 N
If you were on a different planet, the gravitational acceleration would change. This would alter the ball’s weight but not its mass.
Location Effects
The location where you measure the weight of a bowling ball also matters. On the Earth’s surface, gravity is relatively constant. But small variations exist depending on altitude and latitude. At higher altitudes, gravity is slightly weaker. This means:
- A bowling ball weighs less at higher altitudes.
- Close to the poles, gravity is slightly stronger.
For example, if you measure the weight of a bowling ball at sea level and then on a mountain, you will notice a difference. On top of a mountain, the ball weighs a tiny bit less. Here is a small comparison:
| Location | Gravitational Acceleration (m/s²) | Weight of 7 kg Bowling Ball (N) |
|---|---|---|
| Sea Level | 9.8 | 68.6 |
| High Altitude | 9.7 | 67.9 |
This table shows how weight can vary with location. While the difference is small, it is an interesting phenomenon. Always remember, mass remains constant but weight varies with location and gravity.
Credit: www.teachstarter.com
Common Misconceptions
Understanding the difference between the mass and weight of a bowling ball is important. Many people get confused because they seem similar. Yet, they are not the same. These differences are easy to understand with simple explanations. Let’s dive into some common misconceptions and learn more.
Interchangeable Terms
Many people think that mass and weight are the same. They use the terms interchangeably. Yet, they mean different things.
Mass is the amount of matter in an object. It does not change, no matter where the object is. For example, a bowling ball has the same mass on Earth and on the Moon.
Weight, however, is different. Weight is the force of gravity on an object. It changes based on where the object is.
Here are some key points:
- Mass remains constant.
- Weight depends on gravity.
| Mass | Weight |
|---|---|
| Constant | Changes with gravity |
| Measured in kilograms | Measured in newtons |
Understanding these points can help clear up confusion. Mass is not the same as weight. They are different properties.
Weight In Space
Weight changes when an object is in space. In space, gravity is much weaker than on Earth. So, a bowling ball would weigh less.
Imagine an astronaut holding a bowling ball in space. The ball still has the same mass. It is still hard to push or pull. But it feels weightless.
Here is a comparison:
- On Earth, a bowling ball weighs about 70 newtons.
- In space, it weighs almost nothing.
But remember, the mass of the bowling ball does not change. It is still the same object. Only the weight changes because gravity is different.
This is why astronauts can float in space. They do not feel the pull of gravity like we do on Earth. This concept explains why weight and mass are not the same.
Real-world Applications
Understanding the difference between the mass and weight of a bowling ball is important. Mass is the amount of matter in the ball. Weight is the force exerted by gravity on the ball. These differences have significant real-world applications in various fields. This includes sports science and manufacturing standards.
Sports Science
In sports science, the concepts of mass and weight play a crucial role. A bowling ball’s mass remains constant, while its weight can change. This depends on the gravitational pull. For instance, a ball will weigh less on the moon than on Earth.
Why is this important in bowling?
- The mass affects how the ball moves.
- The weight influences how a player handles the ball.
In professional bowling, the ball’s mass is a key factor in predicting its path. A heavier ball (more mass) can knock down more pins. But, it requires more strength to throw. A lighter ball (less mass) may be easier to control. But, it might not knock down as many pins.
- Athletes train with balls of different masses.
- This helps in building strength and technique.
- Coaches analyze how weight affects a player’s performance.
Manufacturing Standards
In the manufacturing of bowling balls, strict standards are followed. These standards ensure consistency and fairness in the sport. Manufacturers need to understand both the mass and weight of the ball.
- The mass must be within a certain range.
- The weight distribution must be even.
- The materials used can affect both mass and weight.
Bowling ball makers use precise measurements. They ensure each ball meets the required standards. This includes testing the ball’s mass and weight under different conditions. For example, they may test the ball in different climates to see how it performs.
- Each ball is checked for consistency.
- Both mass and weight are verified.
- Defective balls are discarded or reworked.
Understanding these differences helps manufacturers produce better quality bowling balls. It ensures players have the best tools for their games. This helps maintain the integrity of the sport.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Mass Of A Bowling Ball?
Mass of a bowling ball is the amount of matter it contains. It is measured in kilograms.
What Is Weight Of A Bowling Ball?
Weight of a bowling ball is the force exerted by gravity on its mass. It is measured in newtons.
Do Mass And Weight Change?
Mass remains constant regardless of location. Weight changes with gravity; it differs on Earth and the Moon.
How To Measure A Bowling Ball’s Mass?
Use a balance scale to measure a bowling ball’s mass. It gives an accurate reading in kilograms.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between mass and weight is important. Mass measures the amount of matter. Weight measures the force of gravity on that matter. A bowling ball’s mass stays the same. Its weight changes with gravity. This knowledge helps in many fields.
Science. Engineering. Everyday life. Recognize these differences. It makes understanding physical properties simpler. So, next time you hold a bowling ball, think about mass and weight. Simple concepts with big impacts. Happy learning!

Passionate Bowler and Bowling Enthusiast
Jess Pinelli is a dedicated bowling enthusiast with a deep love for the sport that spans over 6 years. With numerous strikes, spares, and a few gutter balls under hes belt, he has honed his skills on lanes across the country. Pinelli’s journey in the world of bowling has been a remarkable one, from casual weekend games with friends to competitive league play and even a few local tournaments.
Driven by her passion for the game, Pinelli decided to channel her expertise and knowledge into the digital realm, becoming a prolific author on this bowling website. She’s your go-to source for everything bowling-related, from mastering the perfect hook to choosing the right bowling ball and even navigating the world of bowling etiquette.
When she’s not busy writing informative articles or reviewing the latest bowling gear, you’ll likely find Pinellis at her favorite local bowling alley, helping newcomers improve their game or enjoying some friendly competition with fellow bowlers. She firmly believes that bowling is not just a game but a community, and she’s committed to fostering that sense of camaraderie both online and offline.



